The Fatigue Damage Spectrum (FDS) serves as a pivotal tool in the assessment of structural integrity, portraying the relationship between damage and natural frequency across the frequency domain. Its utility extends to testing laboratories, empowering them to craft precise Random vibration test profiles by analyzing acceleration vibration data derived from real-world environments. By using the FDS, these labs can accurately delineate the damage experienced by structures under dynamic loads, facilitating the development of robust testing protocols essential for ensuring product reliability and safety.
Read MoreMultiple shaker systems are typically used for vibration testing when the unit under test (UUT) is too long or too heavy to test with a single shaker. This approach overcomes the limitations of high drive requirements with a single shaker test. Multiple shaker systems also allow the UUT to be tested in various configurations and directions in the horizontal and vertical orientations.
Read MoreShaker applications involve the use of many attachments to the shaker’s armature. Head expanders, fixtures, adapters, and devices under test (DUT’s), all attach to the shaker for the testing process. While it is common to simply consider the added mass of these components, their deformation during vibration can also have a significant impact on the vibrations experienced at any certain point of interest.
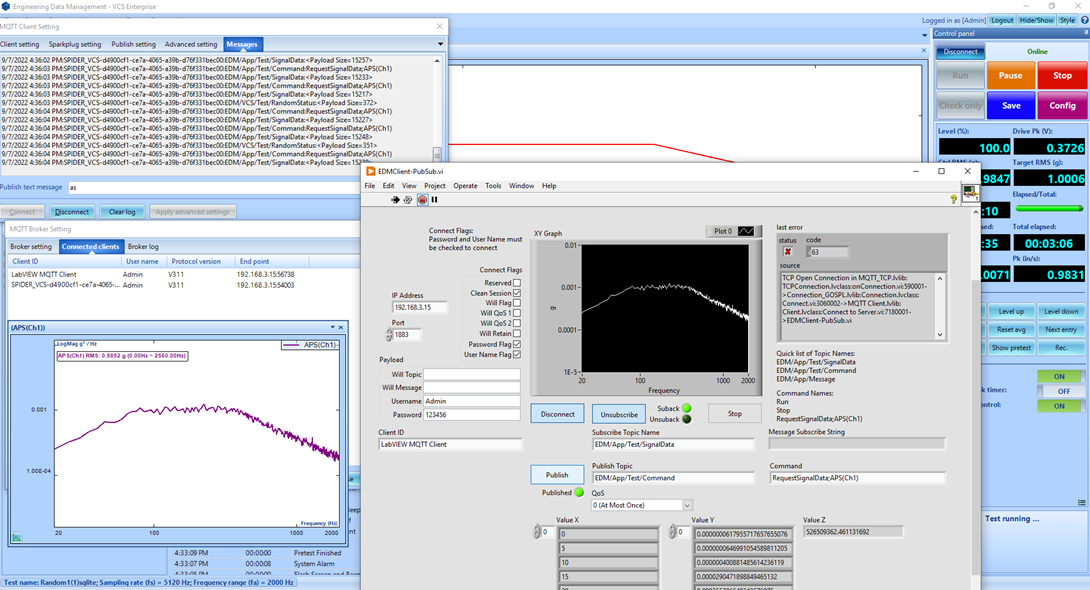
Read MoreUsers can monitor the status of environmental tests (vibration, temperature, humidity) operating in EDM VCS, measurements taken in EDM DSA, and remotely located tests by implementing MQTT in EDM.
Read MoreThe new Transducer Calibration Software helps ensure accurate vibration test measurements by simplifying the calibration process, saving time, and confirming that measurements are performed within specifications.
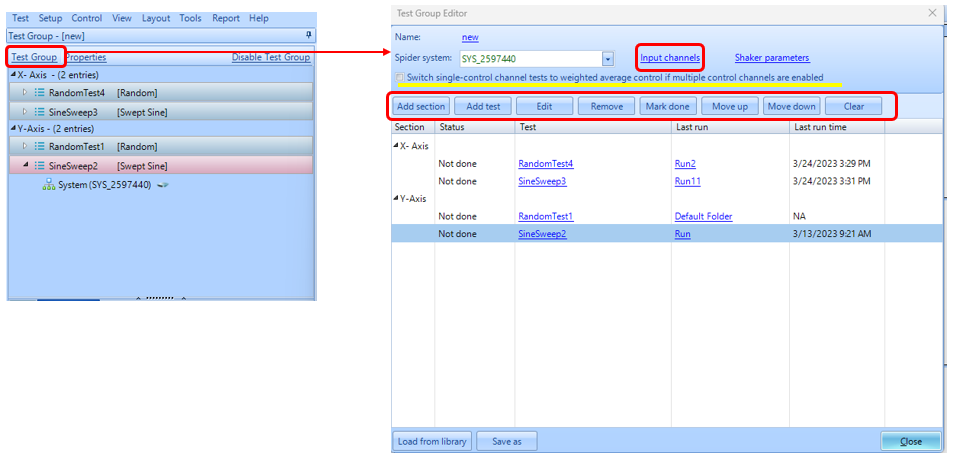
Read MoreThis article discusses a new EDM 11.0 release feature called Test Group, which organizes multiple tests into sections, to run in sequence, and shares test configurations. EDM allows users to configure and re-use the same test for the same or different objects. All configurations and test parameters are applied to a single test. Settings can be loaded and applied to a new test from a saved library. Test configurations are easily shared by sharing just the test file.
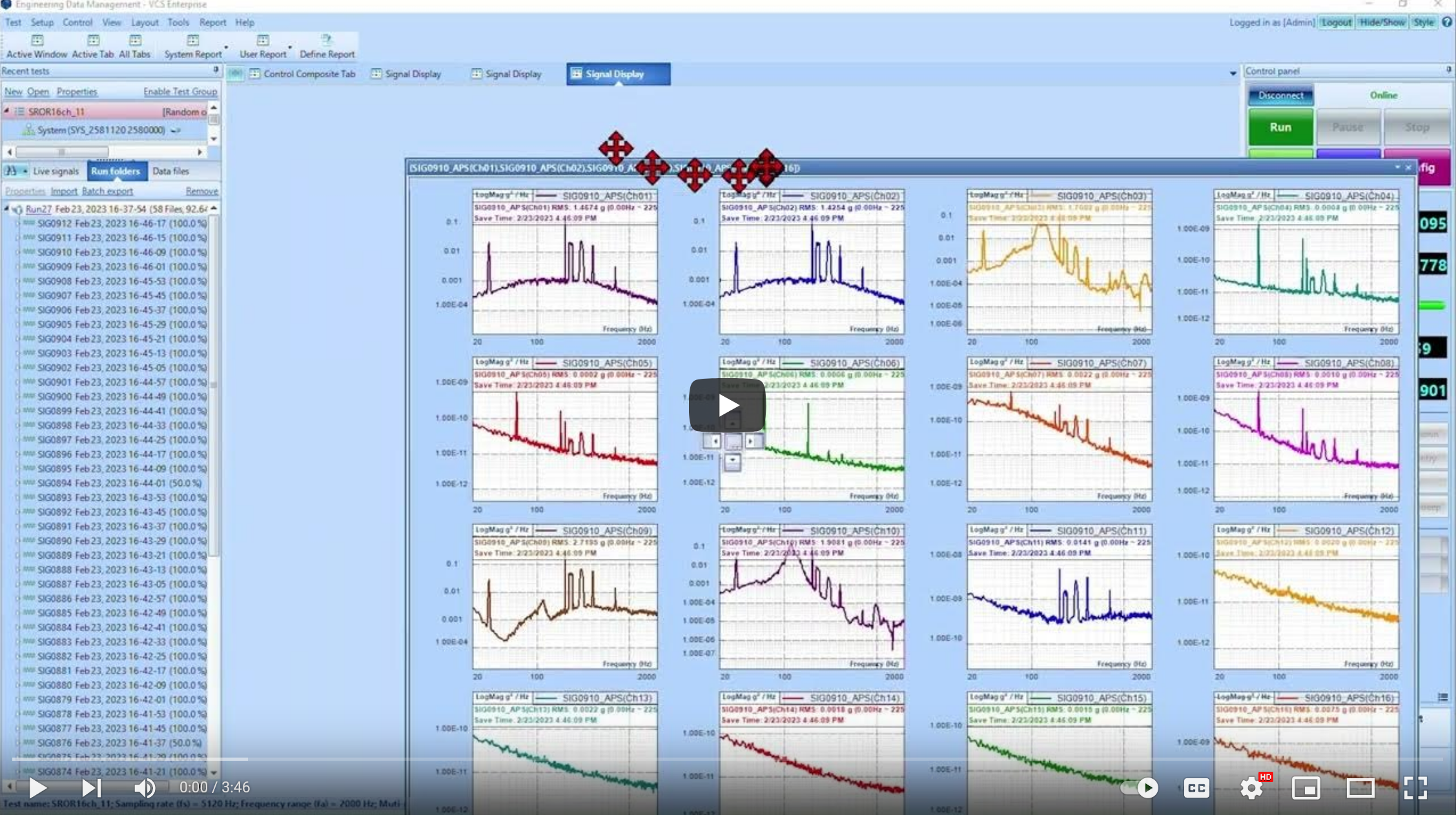
Read MoreUpdated signal display features in Engineering Data Management (EDM) software, version 11.0 allows users to quickly add many signals in stack plots and individual plots.
Read MoreImplementing MQTT in EDM allows users to remotely monitor and operate environmental tests (vibration, temperature, humidity) and take measurements using EDM DSA.
Read MoreThe implementation of MQTT in EDM allows users to monitor the status of environmental tests (vibration, temperature, humidity) executed in EDM VCS, measurements taken in EDM DSA, and remotely operate a test.
Read MoreThis paper concentrates on the MESA Sine on Random control per MIL STD 810H, method 514.8, annex D, 2.3 category 14. This category governs Sine on Random control for helicopters.
Crystal Instruments designed and released the Spider-80M Multiple-Exciter Single-Axis (MESA) vibration controller in 2018. Further details regarding the MESA testing system are available on the Sentek Dynamics website. Detailed product specifications may be requested from the Crystal Instruments team.
Read MoreShock Response Spectrum (SRS) testing is commonly required for defense applications. The UUTs are tested under significantly high levels of shock waveforms.
The concept of SRS predictive notching was proposed a few years ago to fully test UUTs and ensure their survival experiencing real-world vibrations while protecting it from over testing.
Read MoreDual excitation shaker systems are commonly used to test long or heavy devices under test (DUT). When the device under test is very long or too heavy, a single shaker cannot perform the test because of oversized dimensions or a large driving force. Thus a dual excitation shaker system is arranged as the solution. Users can fix the longer sized or heavy DUT horizontally or vertically on top of a dual excitation shaker system. Common arrangements are horizontal push-push, push-pull, and vertical.
Read MoreHead expanders are commonly used for vertical environmental testing. The purpose of the head expander is to extend the surface area of the shaker top to accommodate units under test (UUTs) with large dimensions for mounting and testing. One of the key parameters is the working frequency range associated with each head expander. The upper frequency is often used instead of the first resonance frequency of the head expander in vibration control tests.
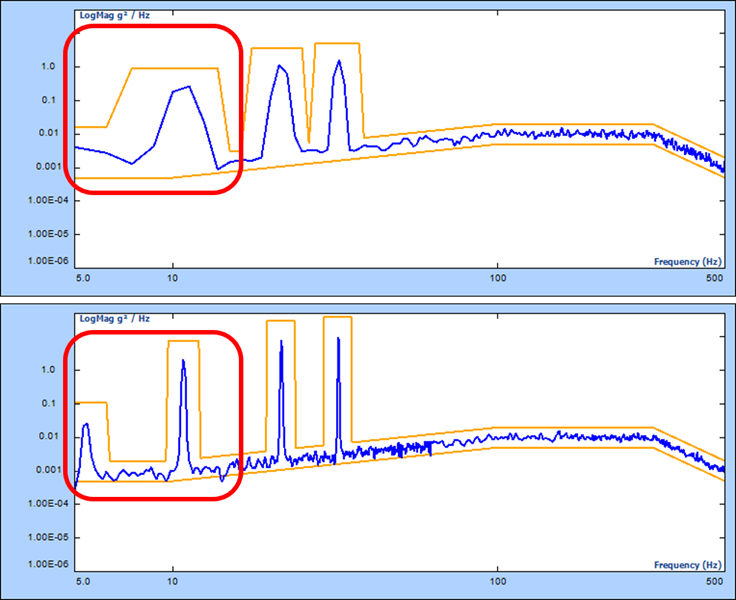
Read MoreIn this blog post, we will discuss the benefits of using Multi-Resolution, a feature available in Vibration Control Systems, to offer a better frequency resolution in the lower frequencies of the Sine-on-Random vibration spectrum. The same benefits are also applied to the general Random test, and Random-on-Random mixed mode test.
Read MoreDigital Input and Output (DIO) is the most popular interface for communicating and interacting with external instruments. Each digital input and output channel has two states: high or low. The Spider can respond to the state of a digital input channel from an external instrument or send a digital output to an external instrument.
Read More